jMock Tutorial for beginners with Test Project
What is jMock?
jMock is a library which helps to create test-driven development of Java code with mock objects.With the help of jMock we can test class independently which depends on another class.
Suppose if one class depends on other class we can create a mock of dependent class and set the initial properties to test the dependent class.
jMock Tutorial Example:
Note: We are using the Eclipse platform for this Test Project. You can download Eclipse from here.
Make sure Java SE Runtime Environment is already installed for Eclipse installer to initiate installation.
Create a Test project in java named Test project.Include following jars in its classpath:
- jmock-2.5.1.jar
- hamcrest-core-1.1.jar
- hamcrest-library-1.1.jar
- JUnit-4.5.jar
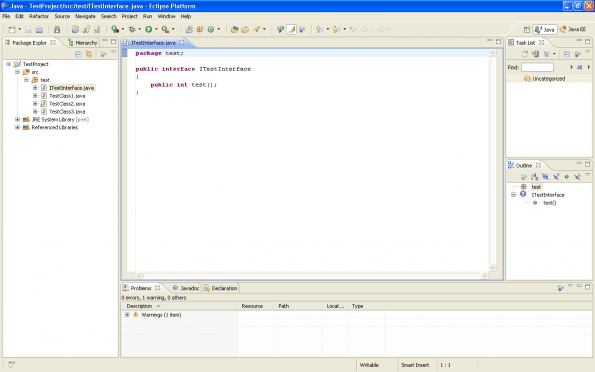
Create an interface named ITestInterface.Put the following code in this interface :
package test;
public interface ITestInterface
{
public int test();
}
Create TestClass1.Put the following code in this class
package test;
public class TestClass1 implements ITestInterface
{
public int test()
{
return 3;
}
}
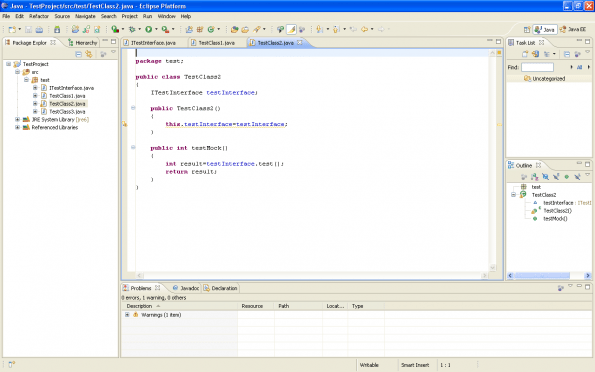
Create TestClass2.Put the following code in this class
package test;
public class TestClass2
{
ITestInterface testInterface;
public TestClass2()
{
this.testInterface=testInterface;
}
public int testMock()
{
int result=testInterface.test();
return result;
}
}
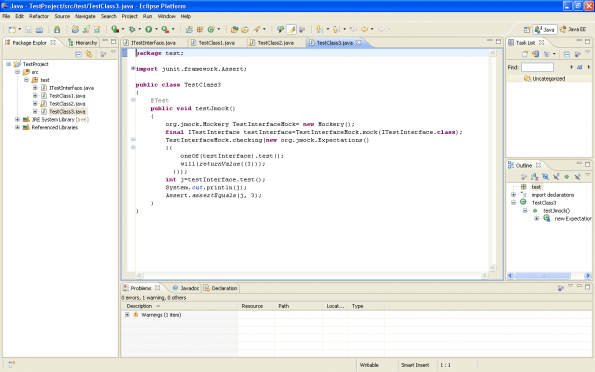
Create TestClass3.Put the following code in this class
package test;
import junit.framework.Assert;
import org.jmock.Mockery;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestClass3
{
@Test
public void testJmock()
{
org.jmock.Mockery TestInterfaceMock= new Mockery();
final ITestInterface testInterface=TestInterfaceMock.mock(ITestInterface.class);
TestInterfaceMock.checking(new org.jmock.Expectations()
{{
oneOf(testInterface).test();
will(returnValue((3)));
}});
int j=testInterface.test();
System.out.println(j);
Assert.assertEquals(j, 3);
}
}
As from above example it is clear that TestClass1 implements the interface ITestInterface. Here if we observe TestClass2 is dependent on TestClass1.So to make it unit testable we are not doing new of TestClass1 in TestClass2.We are using mock object.
In TestClass3 we are making the Mock object of ITestInterface.We are setting the expectation for this object to return 3 when it is called during the unit testing of TestClass2.For example in TestClass3 when we make a call to testInterface.test() the call goes to TestClass2.In TestClass2 when we call testInterface.test() the value is returned by the mock object.In this way we are testing TestClass2 independently.
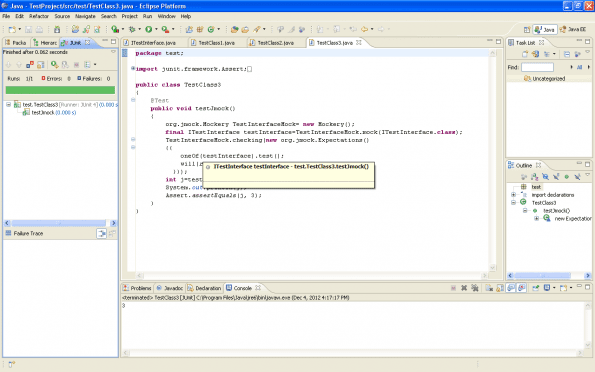
To test above Example right click on TestClass3 and select run as Junit test.
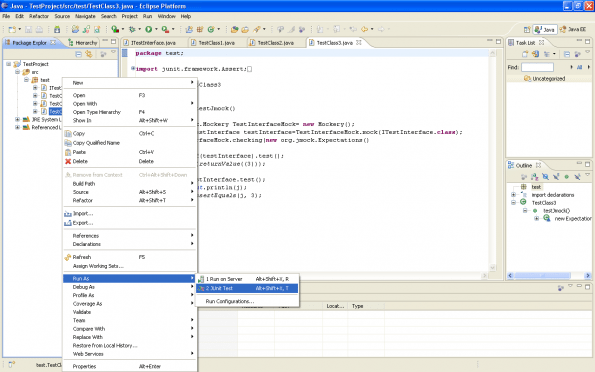 Pin
PinIt will show the following screen:
Test case executed successfully!






5 Responses
Can I know how testclass2 is dependent on testclass1
Thank you sharing the valuable information about jmock! It was a nice read!
You are welcome Tanuja 🙂 Happy to help!
Nice post
Thank you 🙂